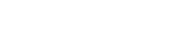Every few years, Nvidia releases a groundbreaking graphics card that pushes PC gaming into a new era. The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 is precisely that—a powerhouse designed to redefine performance standards. Yet, its approach to achieving next-generation performance is unconventional. In many games, the performance improvement over the RTX 4090 isn't as dramatic as one might expect, especially when DLSS Frame Generation is not considered. However, with the latest iteration of Nvidia's DLSS technology, both for upscaling and frame generation, we see significant leaps in image quality and performance that surpass traditional graphics advancements.
The extent to which the Nvidia RTX 5090 will enhance your gaming experience depends on several factors: the games you play, the resolution you use, and your willingness to use AI-generated frames. For those not using a 4K monitor with a 240Hz refresh rate, upgrading might not be necessary. However, if you have a high-end display, the AI-generated frames can truly offer a glimpse into the future of gaming.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 – Photos
 5 Images
5 Images


RTX 5090 – Specs and Features
The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 leverages the Blackwell architecture, which powers high-end data centers and supercomputers, including many advanced AI models. This highlights the RTX 5090's strengths, but Nvidia hasn't overlooked the non-AI aspects of the card.
The RTX 5090 features more Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs) within the same number of Graphics Processing Clusters (GPCs), resulting in an increase to 21,760 CUDA cores from the RTX 4090's 16,384—a 32% increase that significantly boosts raw gaming performance.
Each SM includes four Tensor Cores and one RT Core, like its predecessor, resulting in 680 Tensor Cores and 170 RT cores, compared to 512 and 128 on the RTX 4090. The 5th-generation Tensor Cores enhance AI performance and support FP4 operations, making AI workloads less VRAM-dependent.

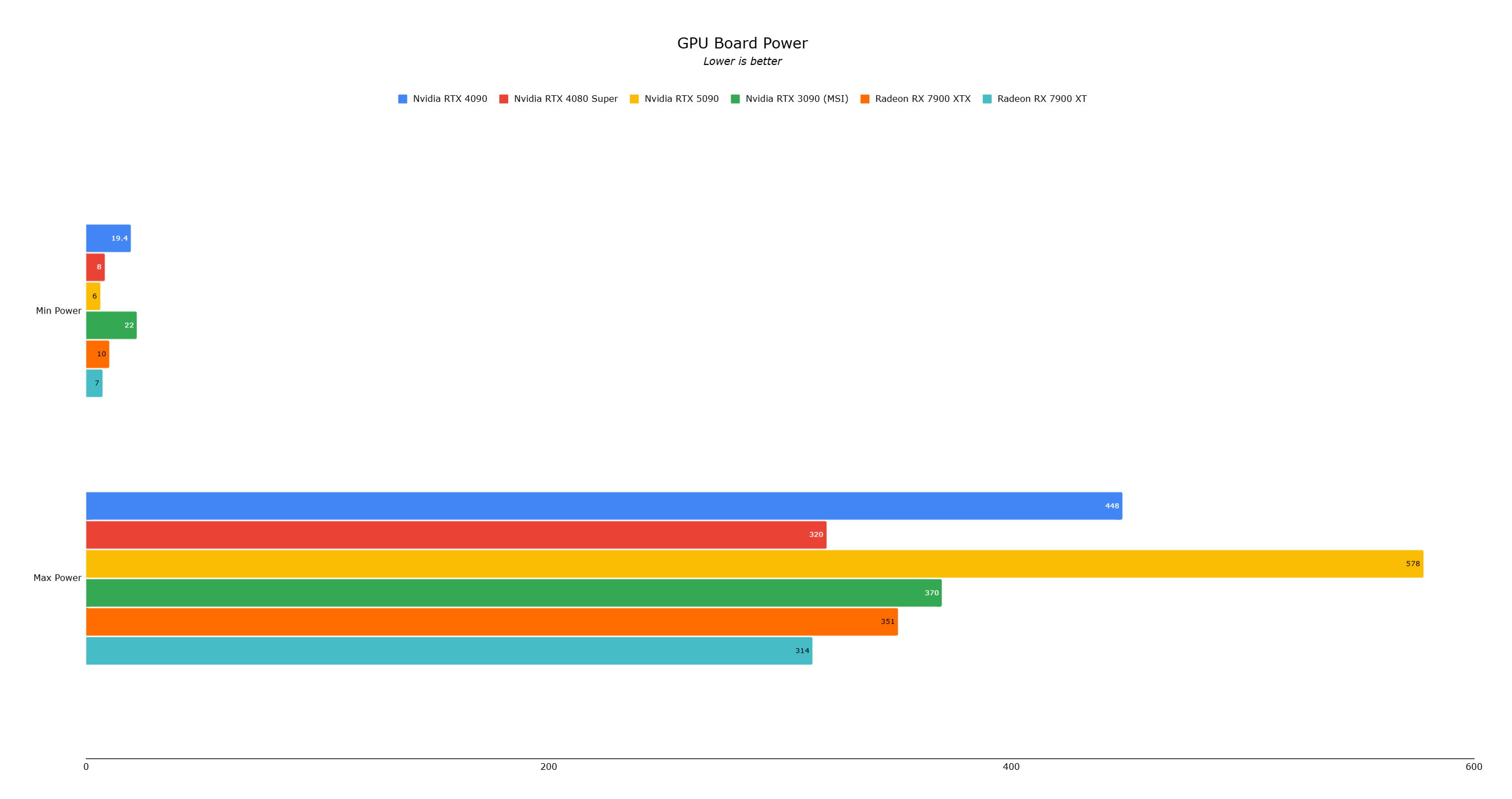
The RTX 5090 is equipped with 32GB of GDDR7 VRAM, a shift from the RTX 4090's GDDR6X, offering faster and more power-efficient memory. Despite requiring 575W of power—a significant jump from the RTX 4090's 450W—power efficiency isn't Nvidia's primary focus with this card.
Nvidia has transitioned the DLSS algorithm to run on a Transformer Neural Network (TNN) for improved image quality and reduced issues like ghosting. Additionally, the introduction of Multi-Frame Generation enhances the frame generation technology from the RTX 4090, allowing multiple frames to be generated from each rendered image for a significant frame rate improvement.
Purchasing Guide
The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 will be available starting January 30, with the Founders Edition priced at $1,999. Note that third-party cards may be priced higher.
The Founders Edition
Despite its 575W power requirement, the RTX 5090 Founders Edition fits into a dual-slot chassis with a dual-fan configuration. The card's temperature peaked at 86°C during testing, higher than the RTX 4090's 80°C but still within safe limits.
Nvidia achieved this by minimizing the PCB and positioning it centrally, flanked by fans that draw air in from the bottom and expel it through the top. The design also features a silver 'X' on the center, a gunmetal-gray chassis, and a white LED 'GeForce RTX' logo.

The RTX 5090 uses a new 12V-2x6 power connector, slightly more efficient than the previous 12VHPWR connector. The angled connector makes installation easier and more secure, and the design allows for use in smaller PC builds.
DLSS 4: Fake Frames?
Nvidia claimed an 8x performance boost with the RTX 5090, primarily through its advanced frame generation capabilities rather than traditional rendering. DLSS 4's Multi-Frame Generation, supported by the new AI Management Processor (AMP) core, allows for efficient frame generation and reduces latency.
The AMP and 5th-generation Tensor Cores enable a new frame generation model that's 40% faster and requires 30% less memory. This model generates three AI frames per rendered frame, with Nvidia's Flip Metering algorithm minimizing input lag.
For optimal performance, DLSS 4 should be enabled when you're already achieving a decent frame rate, ideally paired with DLSS upscaling. At launch, DLSS 4 will be supported in numerous PC games, including beta versions of Cyberpunk 2077 and Star Wars Outlaws.

In testing, the RTX 5090 delivered impressive results in Cyberpunk 2077 at 4K with ray tracing, achieving 94 fps with DLSS on Performance mode, which increased to 162 fps with 2x frame generation and soared to 286 fps with 4x frame generation. Star Wars Outlaws saw similar gains, reaching 300 fps at 4K with DLSS 4 enabled.
While some might dismiss these as 'Fake Frames,' they offer substantial benefits for users with high-refresh, high-resolution displays. Nvidia plans to support DLSS 4 in 75 games by the RTX 5090's launch date.
RTX 5090 – Performance
The RTX 5090 showcases a generational leap in performance, with a 42% increase in 3DMark benchmarks over the RTX 4090. However, real-world gaming performance is often limited by CPU bottlenecks, even with a top-tier Ryzen 7 9800X3D processor.
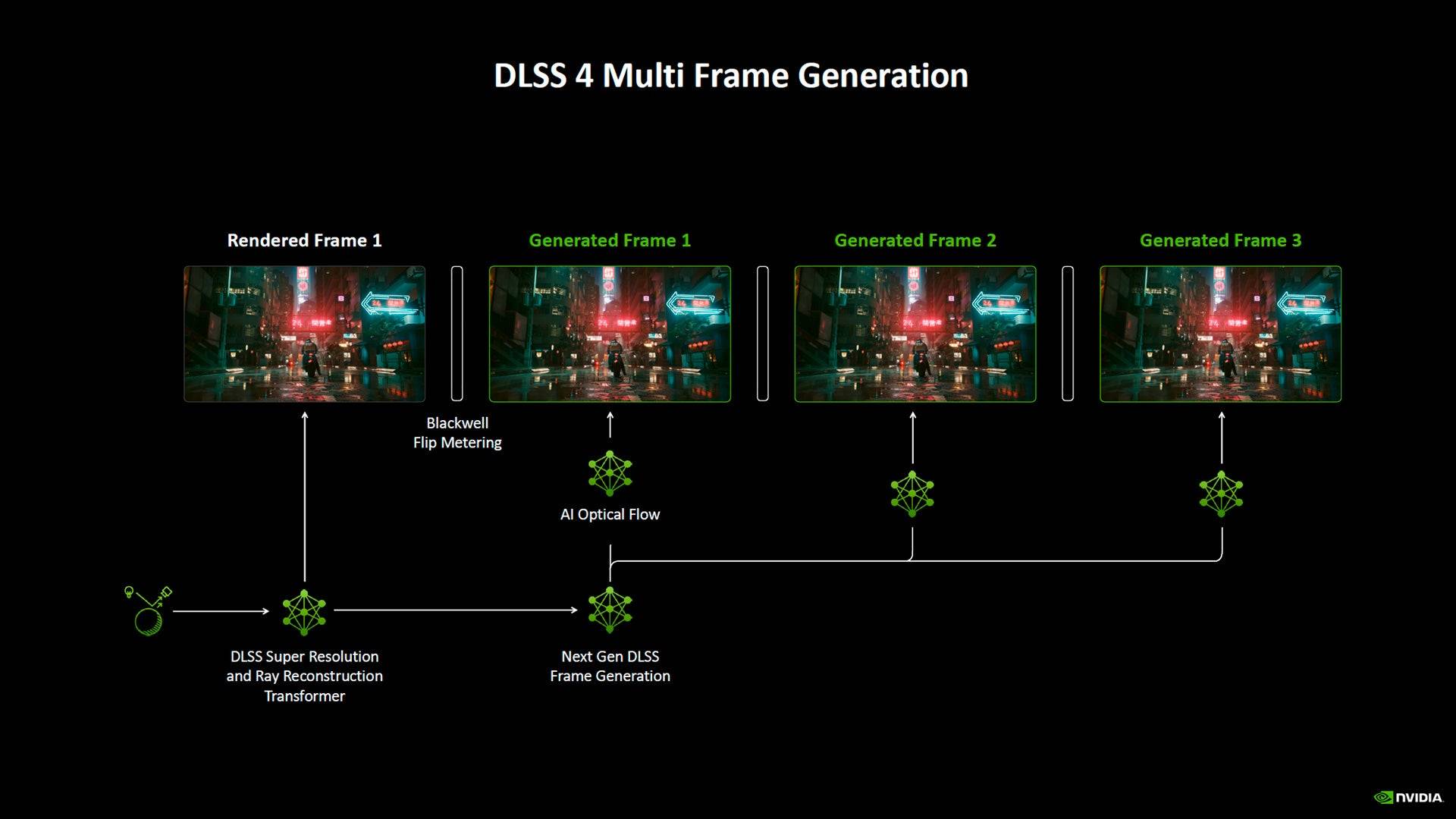
In games like Call of Duty Black Ops 6 and Cyberpunk 2077, the RTX 5090 only shows a modest 10% performance increase over the RTX 4090 at 4K. Metro Exodus: Enhanced Edition saw a more significant 25% improvement, while Red Dead Redemption 2 experienced a mere 6% uplift.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 – Benchmarks
 14 Images
14 Images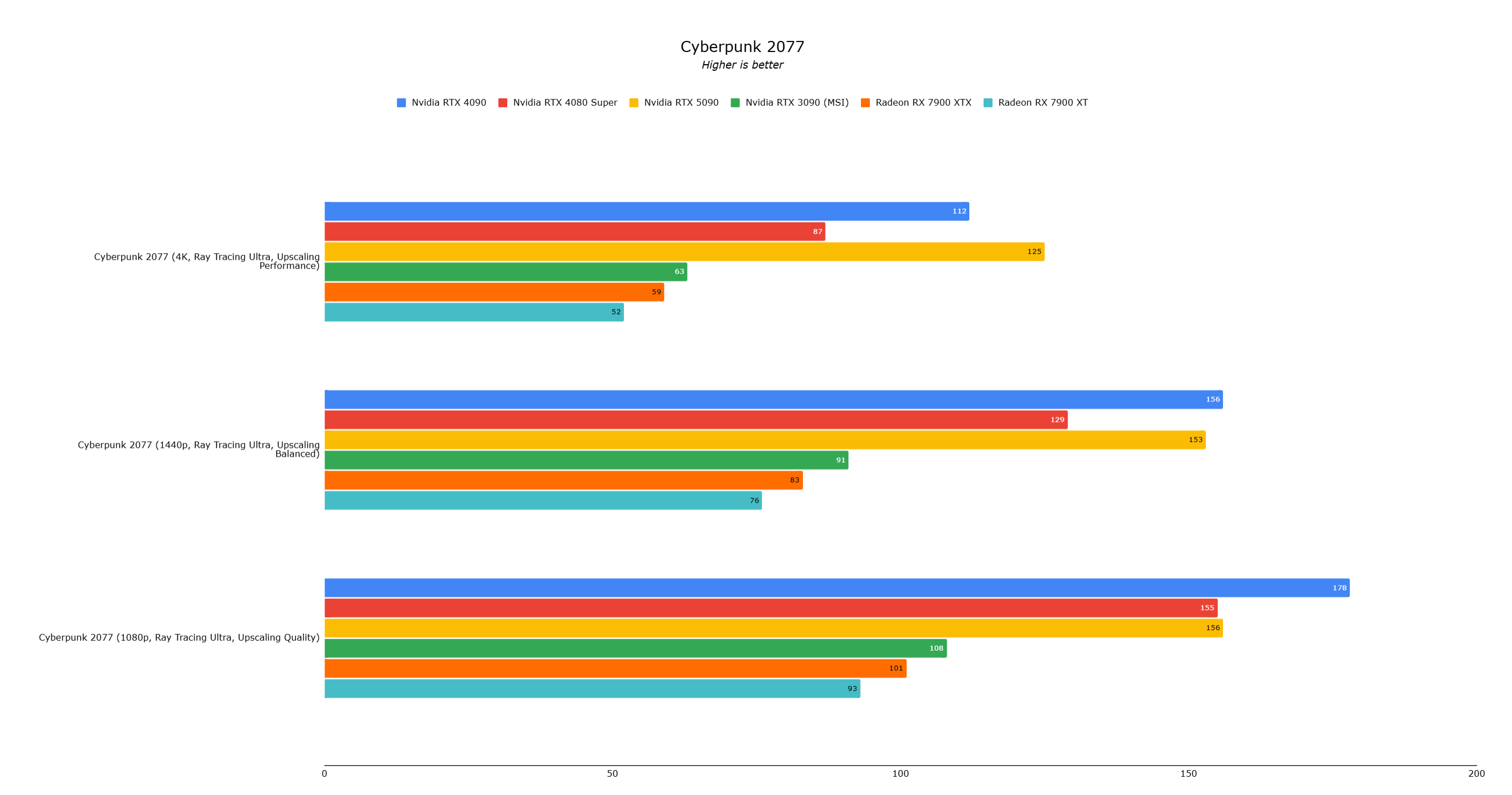
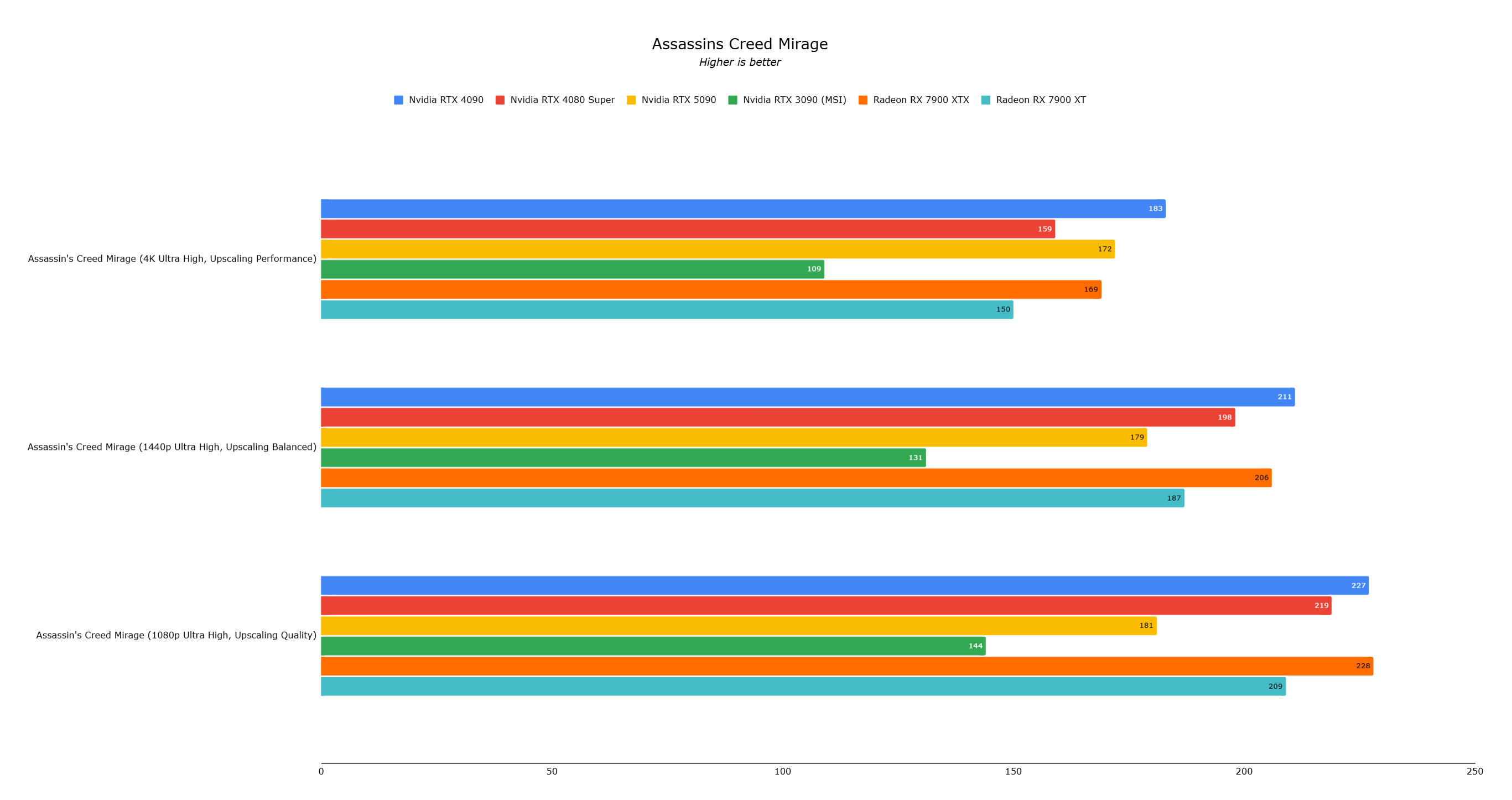
Total War: Warhammer 3, without ray tracing or upscaling, showed a 35% performance improvement, while Assassin's Creed Mirage experienced performance issues likely due to driver bugs.
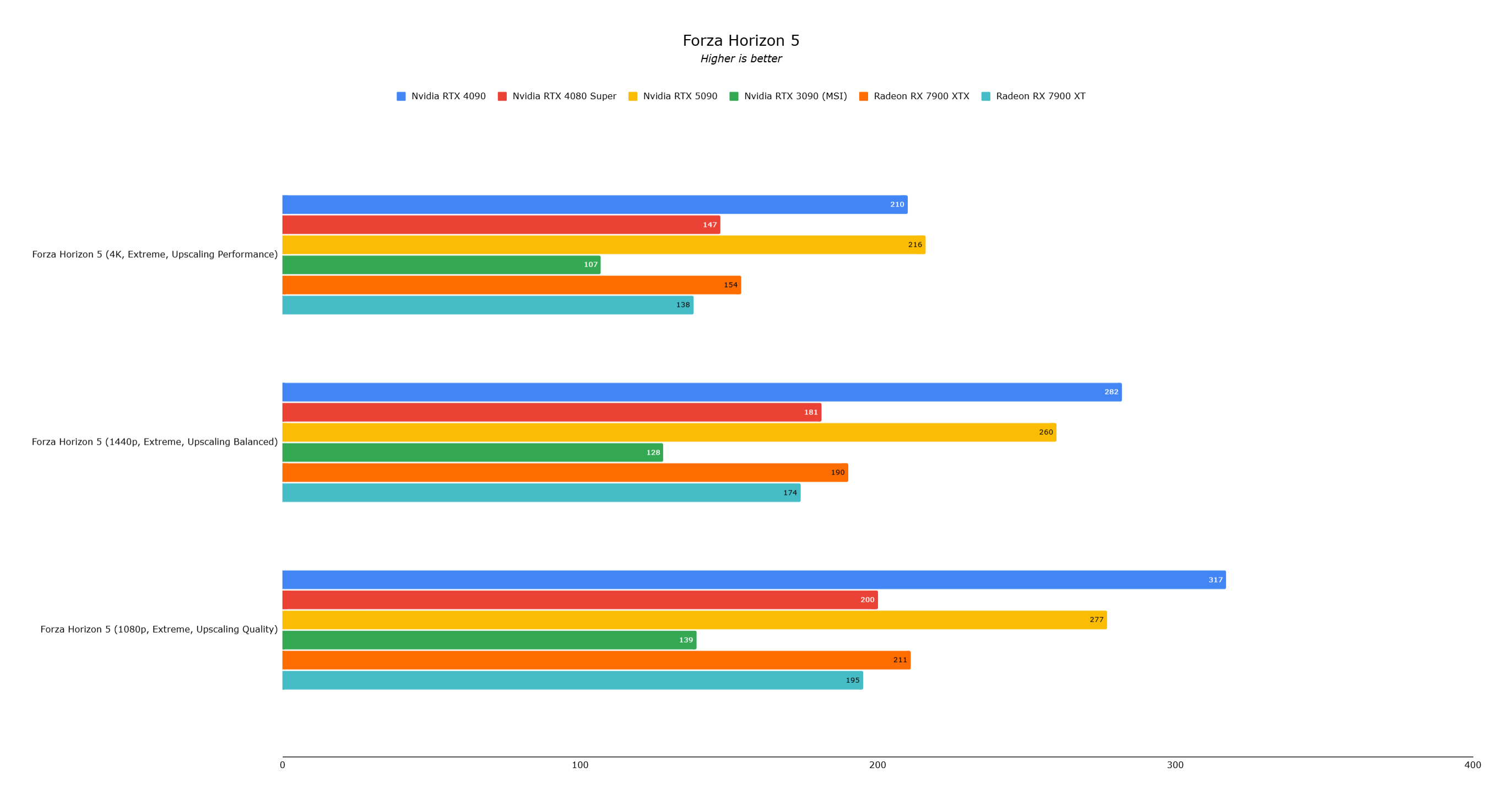
Black Myth: Wukong and Forza Horizon 5 showcased a 20% and negligible performance uplift, respectively, over the RTX 4090.
The RTX 5090 is undoubtedly the fastest consumer graphics card available, but many current games can't fully leverage its capabilities. This positions the RTX 5090 as an investment in the future of AI-powered gaming, particularly for those with high-end setups willing to spend at least $1,999 on cutting-edge technology. For others, the RTX 4090 remains a robust option for the foreseeable future.